Summary
Symptoms
- Pain in the joint
- Stiffness
- Reduced range of motion
Investigations by a doctor may include
- X-Rays
- Ultrasounds
- CT Scan
- MRI Scan
Shoulder Replacement is of two kinds
- Hemi-Arthroplasty – In which only the ball of the upper arm bone is replaced
- Total Shoulder Arthroplasty – In which both the ball and socket are replaced
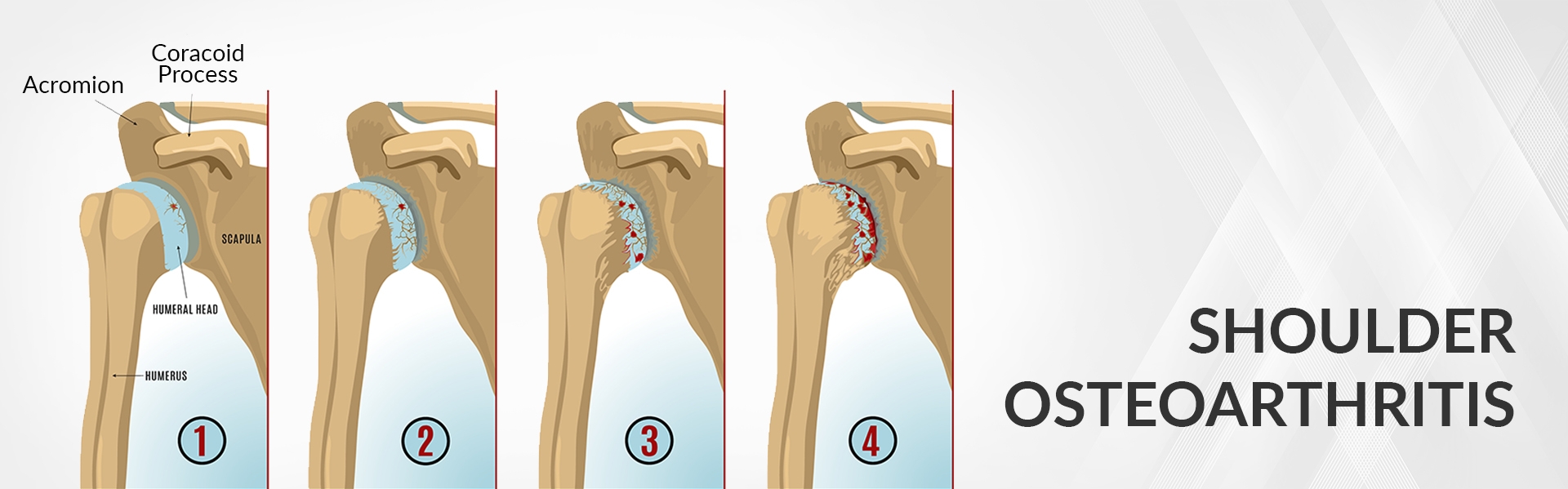
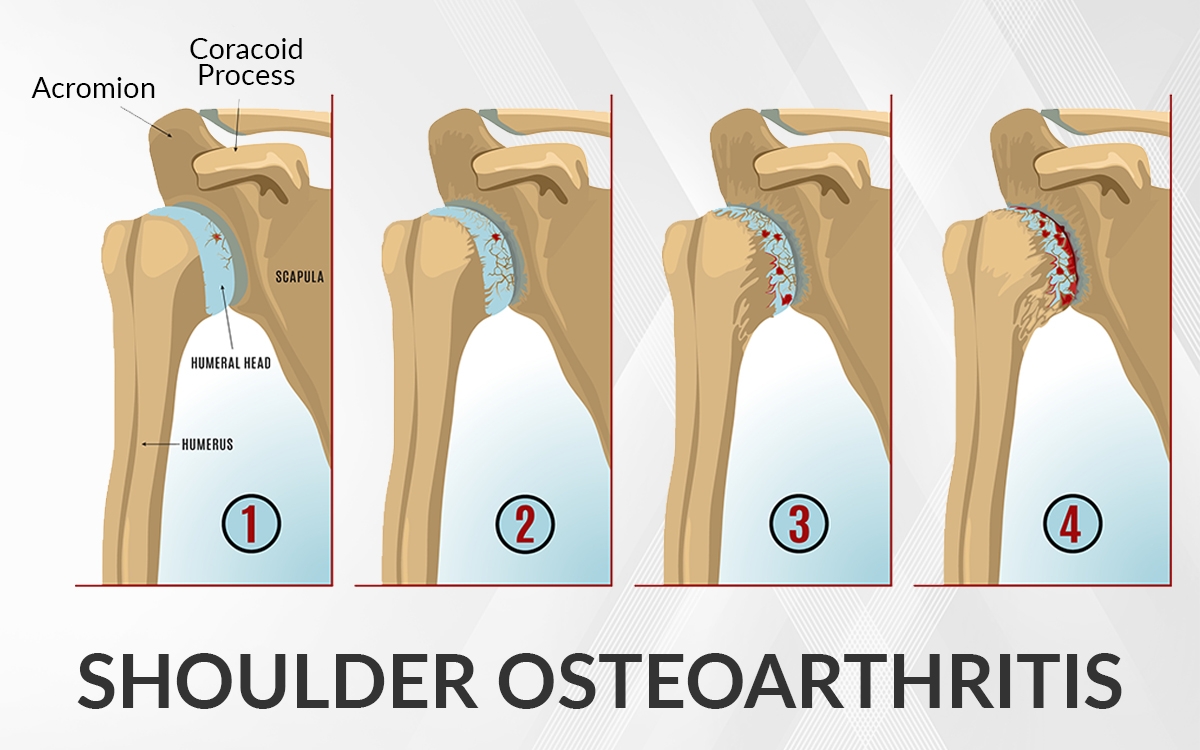
What is Shoulder Arthritis?
Shoulder arthritis occurs when the cartilage starts wearing down on the ball and/or the socket side of the shoulder joint. Symptoms of shoulder arthritis may include pain in the joint, stiffness and reduced range of motion.
What does arthritis in the shoulder feel like?
Most common symptom of shoulder arthritis is pain which is aggravated by activity. This pain progressively worsens. Patients complain of an ache deep in the joint which may intensify with changes in the weather.
Anatomy of shoulder joint
The shoulder is made up of three bones – Your upper arm bone (humerus), shoulder blade (scapula) and your collar bone (clavicle). The head of your upper arm bone fits into the socket in your shoulder blade (glenoid). Muscles and tendons around your shoulder keep your arm bone centred in your shoulder socket. These muscles are known as the rotator cuff.
There are two joints in the shoulder which can both get affected by arthritis. One joint is where clavicle meets the top of the shoulder blade (acromion). This is also known as acromioclavicular joint. The second joint is where the ball of the upper arm bone fits into the socket of the scapula which is known as glenohumeral joint.
Osteoarthritis usually affects people over 50 years of age and is more common in the acromioclavicular joint than the glenohumeral shoulder joint.
Is exercise good for Shoulder Arthritis?
The most beneficial exercise for arthritis includes range of motion and flexibility exercises such as stretches which reduces the stiffness. Exercises that build up the muscle mass around the shoulder joint will also help reduce strain on them.
Can arthritis be removed from the shoulder?
Once the arthritis in the glenohumeral joint becomes advanced and stops responding to the steroid treatment then the answer is a shoulder replacement (like a hip or a knee replacement). In this the damaged parts of the shoulder are removed and replaced with artificial components known as prosthesis. Replacement options include a hemi-arthroplasty in which only the ball of the upper arm bone is replaced and a total shoulder arthroplasty in which both the ball and socket are replaced.
Why is my shoulder pain not going away?
If the pain in your shoulder doesn’t settle down it is time to see your doctor. There are a number of possible causes of shoulder pain but the most common causes of shoulder pain are rotator cuff injuries, rotator cuff tears, rotator cuff impingement and osteoarthritis.
What will the doctor do when I see him?
He will take a detailed history, he will examine your neck and your shoulder joint and do investigations like x-rays. X-rays in arthritic situation will show an uneven loss of cartilage and spurring of the underlying bone. They can also do scans like an ultrasound scan to assess the condition of your muscles around the shoulder joint, a CT scan to assess the bones of your shoulder joint or a MRI scan. Based on your clinical examination and the results of the scans he will then formulate a treatment plan for you.
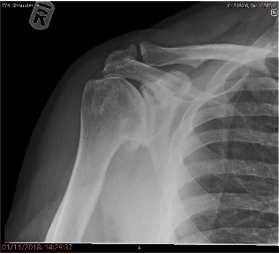
68 years old male, severe arthritis to the right shoulder
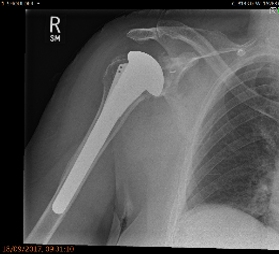
Anatomic Shoulder Replacement done
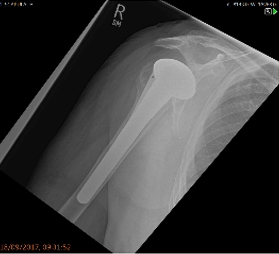
Anatomic Shoulder Replacement done
BMI Chelsfield Park Hospital
Bucks Cross Road Chelsfield ORPINGTON BR6 7RG
01689 877855
BMI The Blackheath Hospital
40-42 Lee Terrace Blackheath LONDON SE3 9UD
020 8318 7722
BMI The Sloane Hospital
125 Albemarle Road BECKENHAM BR3 5HS
020 8466 4000
Princess Royal University Hospital
Farnborough Common ORPINGTON BR6 8ND
01689 863223